Gastrointestinal & Colon Cancers
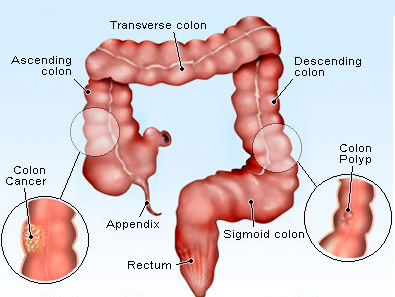
The colon is the part of the digestive system where the waste material is stored. The rectum is the end of the colon adjacent to the anus. Together, they form a long, muscular tube called the large intestine (also known as the large bowel). Tumors of the colon and rectum are growths arising from the inner wall of the large intestine. Benign tumors of the large intestine are called polyps. Malignant tumors of the large intestine are called cancers. Benign polyps do not invade nearby tissue or spread to other parts of the body. Benign polyps can be easily removed during colonoscopy and are not life-threatening. If benign polyps are not removed from the large intestine, they can become malignant (cancerous) over time. Most of the cancers of the large intestine are believed to have developed from polyps. Cancer of the colon and rectum (also referred to as colorectal cancer) can invade and damage adjacent tissues and organs. Cancer cells can also break away and spread to other parts of the body (such as liver and lung) where new tumors form. The spread of colon cancer to distant organs is called metastasis of the colon cancer. Once metastasis has occurred in colorectal cancer, a complete cure of the cancer is unlikely.
